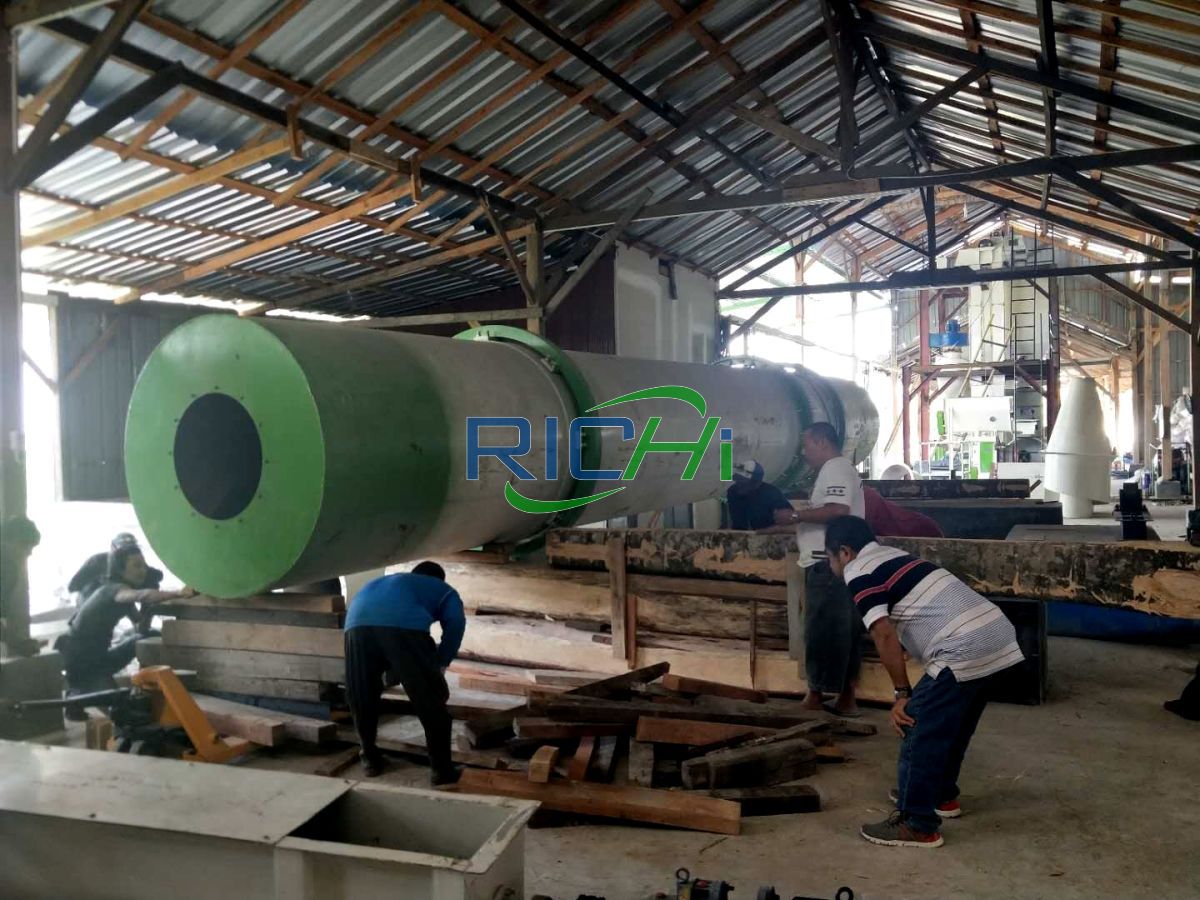
As the world embraces the transition towards renewable and sustainable energy sources, the construction of wood pellet plants has emerged as a crucial endeavor. These specialized facilities play a pivotal role in transforming abundant biomass resources into compact, energy-dense pellets, fueling the growing demand for clean and efficient energy solutions. From site selection to commissioning, the construction of a wood pellet plant is a complex undertaking that requires careful planning, execution, and adherence to stringent standards.
Site Selection and Preparation
The first step in the wood pellet plant construction is the selection of an appropriate site. This decision is influenced by several factors, including proximity to biomass feedstock sources, access to transportation networks, availability of utilities, and compliance with local zoning and environmental regulations. Once the site is chosen, extensive preparation work is required, including land clearing, grading, and the installation of necessary infrastructure such as access roads, utilities, and drainage systems.
Plant Layout and Design
The design of a wood pellet plant is a critical aspect that determines its efficiency, capacity, and overall performance. Experienced engineers and architects collaborate to create a layout that optimizes material flow, minimizes waste, and ensures worker safety. The plant design typically incorporates various sections, including feedstock receiving and storage areas, preprocessing facilities, pellet production lines, cooling and screening systems, and packaging and loading zones.
Feedstock Handling and Preprocessing
A key component of a wood pellet plant is the feedstock handling and preprocessing system. This section is responsible for receiving, storing, and preparing the raw biomass materials for the pelletization process. It typically includes equipment such as conveyors, silos, dryers, and grinding mills. Proper design and construction of these systems are crucial to ensure a consistent and efficient flow of materials throughout the plant.
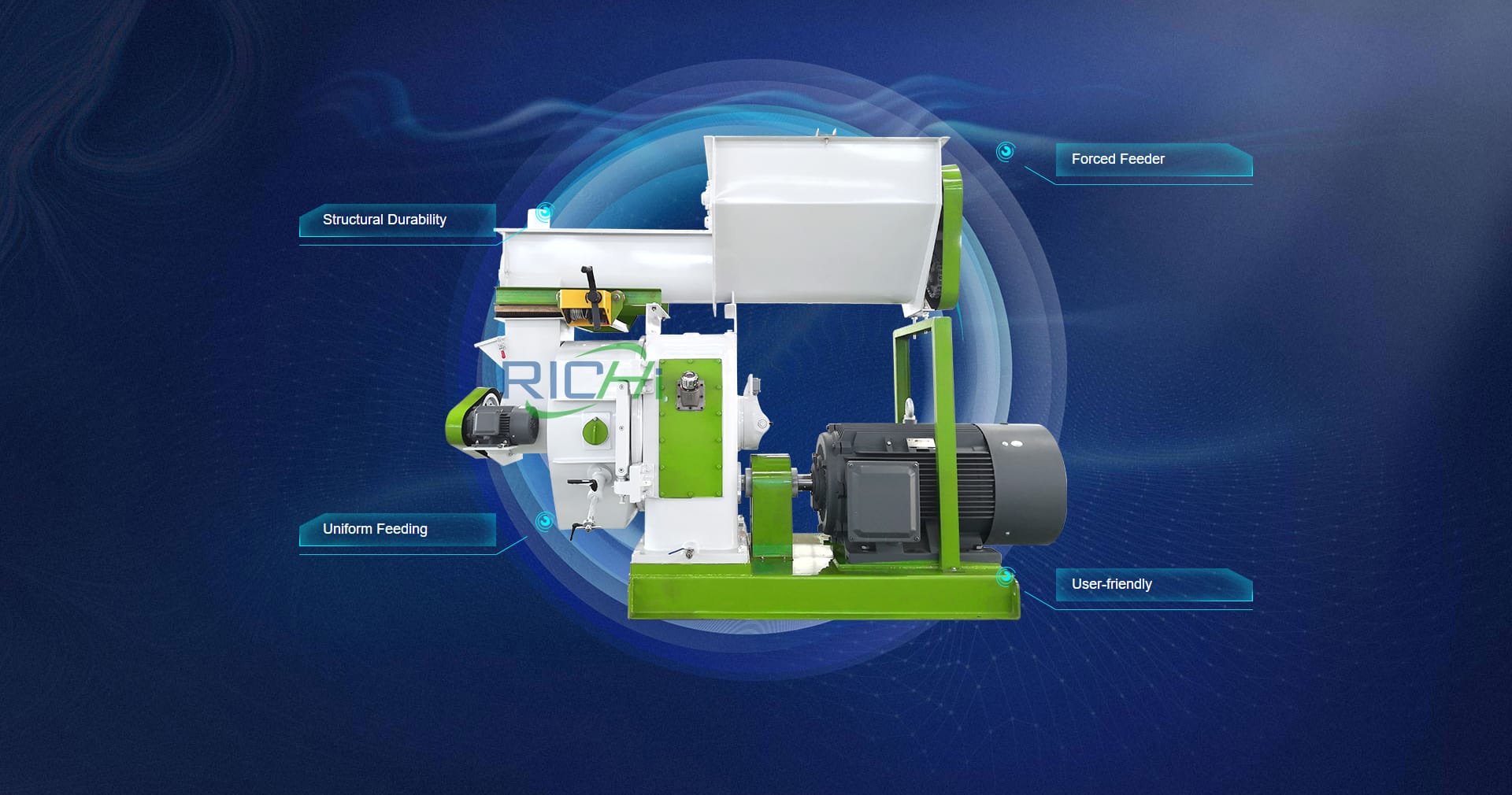
Pellet Production Line
At the heart of a wood pellet plant lies the wood pellet production line, where the magic of transforming biomass into energy-dense pellets takes place. This section houses the specialized machinery responsible for conditioning, pelleting, cooling, and screening the final product. The construction of this area requires meticulous attention to detail, as the performance and reliability of the equipment directly impact the plant’s overall productivity and output quality.
Auxiliary Systems and Infrastructure
In addition to the core production facilities, a wood pellet plant requires various auxiliary systems and infrastructure to support its operations. These include:
- Utilities: Reliable and efficient utility systems, such as electricity, water, and natural gas, are essential for powering the plant and supporting various processes.
- Wastewater Treatment: Proper wastewater treatment facilities are necessary to manage and treat any effluents generated during the production process, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
- Air Pollution Control: Wood pellet plants must incorporate effective air pollution control systems to capture and mitigate particulate matter and other emissions, minimizing their environmental impact.
- Fire Protection: Due to the combustible nature of the materials involved, robust fire protection systems, including sprinklers, fire alarms, and suppression equipment, are critical for ensuring the safety of the plant and its workers.
- Control and Monitoring Systems: Advanced control and monitoring systems are implemented to oversee and optimize the various processes within the plant, ensuring efficient operation and adherence to quality standards.
Construction Challenges and Considerations
The construction of a wood pellet plant is not without its challenges. One significant consideration is the management of dust and emissions during the construction phase, as the handling of biomass materials can generate significant amounts of particulate matter. Proper dust control measures, such as enclosures, water suppression systems, and personal protective equipment, must be implemented to safeguard worker health and minimize environmental impact.
Another challenge lies in the coordination and integration of various specialized systems and equipment from different suppliers. Effective project management and communication are crucial to ensure seamless integration and avoid delays or compatibility issues.Additionally, the construction process must comply with stringent safety regulations and industry best practices to protect the well-being of workers and ensure the long-term integrity of the plant.
Commissioning and Start-up
Once the construction phase is complete, the wood pellet plant undergoes a rigorous commissioning and start-up process. This stage involves thorough testing and verification of all systems, equipment, and processes to ensure they meet the design specifications and operational requirements. Comprehensive training programs are implemented to equip the plant personnel with the necessary knowledge and skills to operate and maintain the facility safely and efficiently.
Continuous Improvement and Sustainability
The construction of a wood pellet plant is not the end of the journey but rather the beginning of a continuous pursuit of improvement and sustainability. Regular maintenance, upgrades, and optimization of processes are essential to maintain the plant’s efficiency, productivity, and environmental performance.
Additionally, exploring opportunities for energy conservation, waste reduction, and the integration of renewable energy sources can further enhance the plant’s sustainability credentials.As the world continues its transition towards a more sustainable energy future, the construction of wood pellet plants will play an increasingly vital role in harnessing the potential of biomass resources.
By adhering to best practices, embracing innovation, and prioritizing environmental stewardship, these facilities will not only contribute to the production of clean and renewable energy but also pave the way for a greener and more resilient tomorrow.