As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and the need for sustainable energy sources, the demand for wood pellets has skyrocketed. These compact, densified biomass fuel pellets offer a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels, and their production relies heavily on the efficiency and performance of wood pellet mills.
The Rise of Wood Pellets as a Renewable Energy Source
Wood pellets are a versatile and efficient fuel source, widely used in residential and commercial heating systems, as well as in industrial applications such as co-firing in coal-fired power plants. Compared to traditional firewood, wood pellets offer several advantages, including:
- Higher energy density: Wood pellets are densely compacted, allowing for more efficient transportation and storage.
- Consistent quality: Pellets are produced from a variety of wood sources, ensuring a consistent and uniform fuel source.
- Reduced emissions: When burned, wood pellets produce lower levels of particulate matter and greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuels.
- Renewable and sustainable: Wood pellets are made from renewable biomass sources, such as sawmill residues, forest thinnings, and agricultural waste.
As the demand for sustainable energy solutions continues to grow, the wood pellet industry has experienced a significant surge, driving the need for efficient and reliable wood pellet mills.
The Intricate Workings of a Wood Pellet Mill
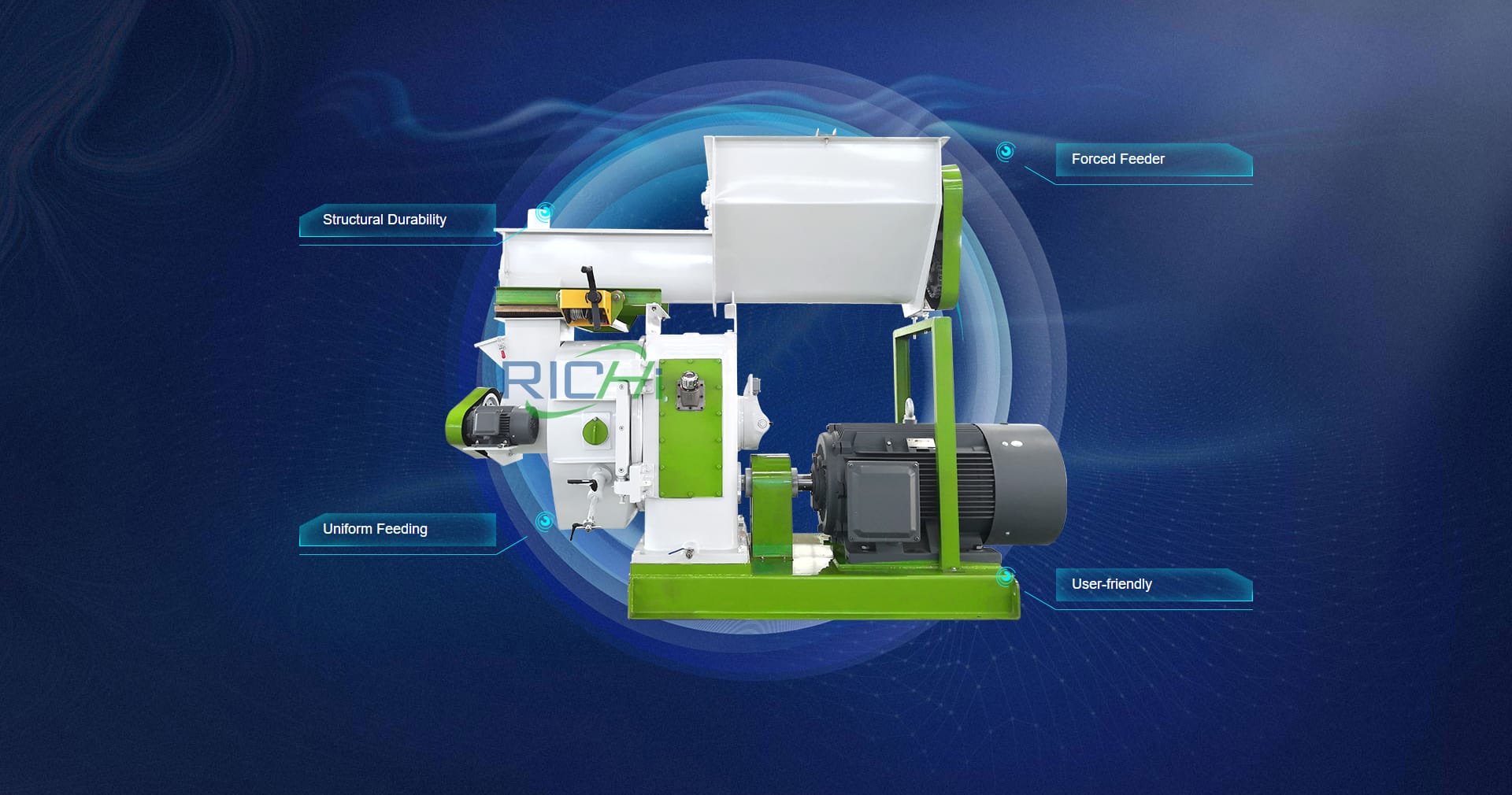
A wood pellet mill is a specialized machine designed to compress and extrude biomass materials, such as sawdust, wood shavings, and other woody residues, into compact, cylindrical pellets. The process of wood pellet production line typically involves several key stages:
- Raw Material Preparation: The raw biomass materials are first dried to reduce moisture content, ensuring efficient pellet production and preventing degradation during storage.
- Grinding and Sizing: The dried biomass is then fed into a grinding mill, such as a hammer mill or a disk mill, where it is reduced to a consistent particle size, typically between 3-6 mm.
- Conditioning: The ground material is conditioned with steam or water to increase its temperature and moisture content, facilitating the binding of the particles during the pelleting process.
- Pelleting: The conditioned material is fed into the pellet mill, where it is compressed and extruded through small die holes by rotating rollers or a ring die. The resulting pellets are cut to the desired length by knives or a die.
- Cooling and Drying: After pelleting, the hot pellets are rapidly cooled and dried to prevent further moisture absorption and maintain their structural integrity.
- Screening and Packaging: The cooled pellets are screened to remove any fines or oversized pellets, ensuring a consistent product. Finally, the pellets are packaged or loaded into bulk containers for distribution and storage.
Factors Influencing Pellet Quality and Efficiency
The quality and efficiency of a wood pellet mill are influenced by several critical factors, including:
- Raw Material Quality: The type and quality of the biomass feedstock significantly impact the pellet quality and production efficiency. Consistent and uniform raw materials are essential for optimal performance.
- Particle Size Distribution: Achieving a uniform particle size distribution through proper grinding is crucial for efficient pelleting and pellet durability.
- Conditioning Parameters: The temperature, moisture content, and conditioning time play a vital role in determining pellet quality, durability, and energy consumption during the pelleting process.
- Die Specifications: The size, shape, and compression ratio of the die holes in the pellet mill affect the physical characteristics and density of the pellets, as well as the energy requirements for the pelleting process.
- Cooling Rate: Rapid and efficient cooling is necessary to prevent pellet degradation and maintain structural integrity, ensuring a consistent and high-quality product.
- Maintenance and Optimization: Regular maintenance and optimization of the wood pellet mill, including die replacement, roller adjustment, and process parameter tuning, are essential for maintaining optimal performance and efficiency.
Advancements and Future Outlook
The wood pellet mill industry is continuously evolving, driven by the need for increased efficiency, automation, and sustainability. Advancements in areas such as process control, energy optimization, and alternative biomass sources are shaping the future of wood pellet production.
One notable development is the integration of advanced technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and machine learning, into wood pellet mills. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and optimized process control, further enhancing the performance and efficiency of the machinery.
Additionally, the industry is exploring the use of alternative biomass sources, such as agricultural residues, energy crops, and municipal solid waste, as potential feedstocks for wood pellet production. These alternative sources not only contribute to the sustainability of the industry but also provide opportunities for diversification and resource utilization.
As the global demand for renewable energy sources continues to rise, the role of wood pellet mills will become increasingly crucial in meeting the world’s energy needs while promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly practices. With ongoing research and innovation, these machines will continue to evolve, ensuring the biomass energy industry can meet the growing demand for clean, efficient, and reliable energy solutions.