As the world transitions towards a more sustainable and renewable energy future, biomass pellets have emerged as a promising solution, offering a clean and efficient alternative to fossil fuels. However, the successful implementation of biomass pellet projects hinges on a thorough understanding of the associated costs, which can vary significantly depending on various factors. In this article, we delve into the intricate cost landscape of biomass pellet projects, shedding light on the key components and considerations that shape their financial viability.
The Cost Components of Biomass Pellet Projects
Biomass pellet plant projects encompass a range of cost elements, each playing a crucial role in determining the overall project expenditure. These components can be broadly categorized as follows:
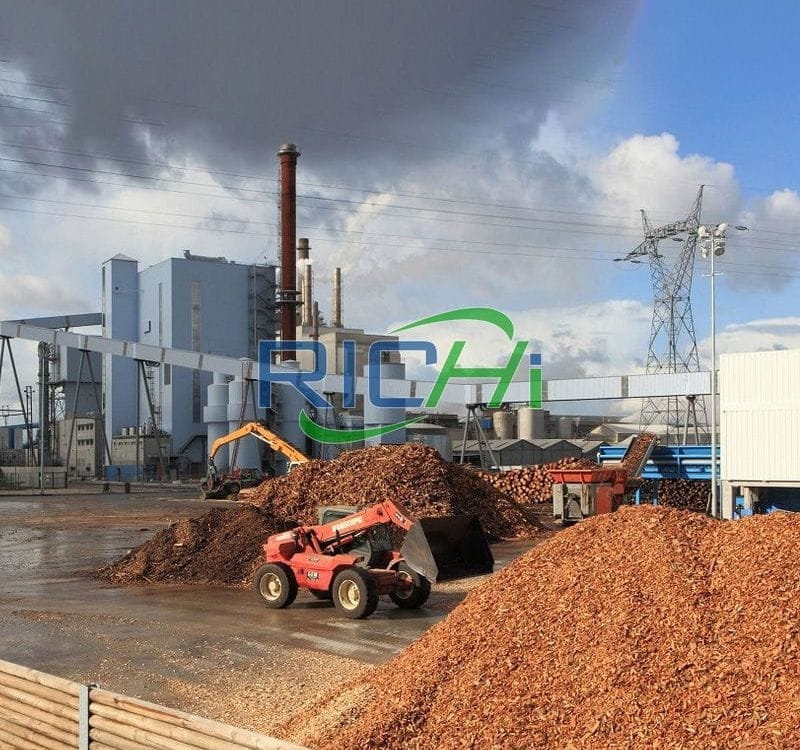
- Feedstock Costs: The cost of procuring and transporting the raw biomass materials, such as wood residues, agricultural waste, or dedicated energy crops, is a significant factor in the overall project cost. The availability, quality, and proximity of the feedstock sources can significantly impact these costs.
- Preprocessing Costs: Before the biomass can be converted into pellets, it often requires preprocessing steps, such as drying, grinding, and sizing. These processes involve specialized equipment and energy consumption, contributing to the overall project costs.
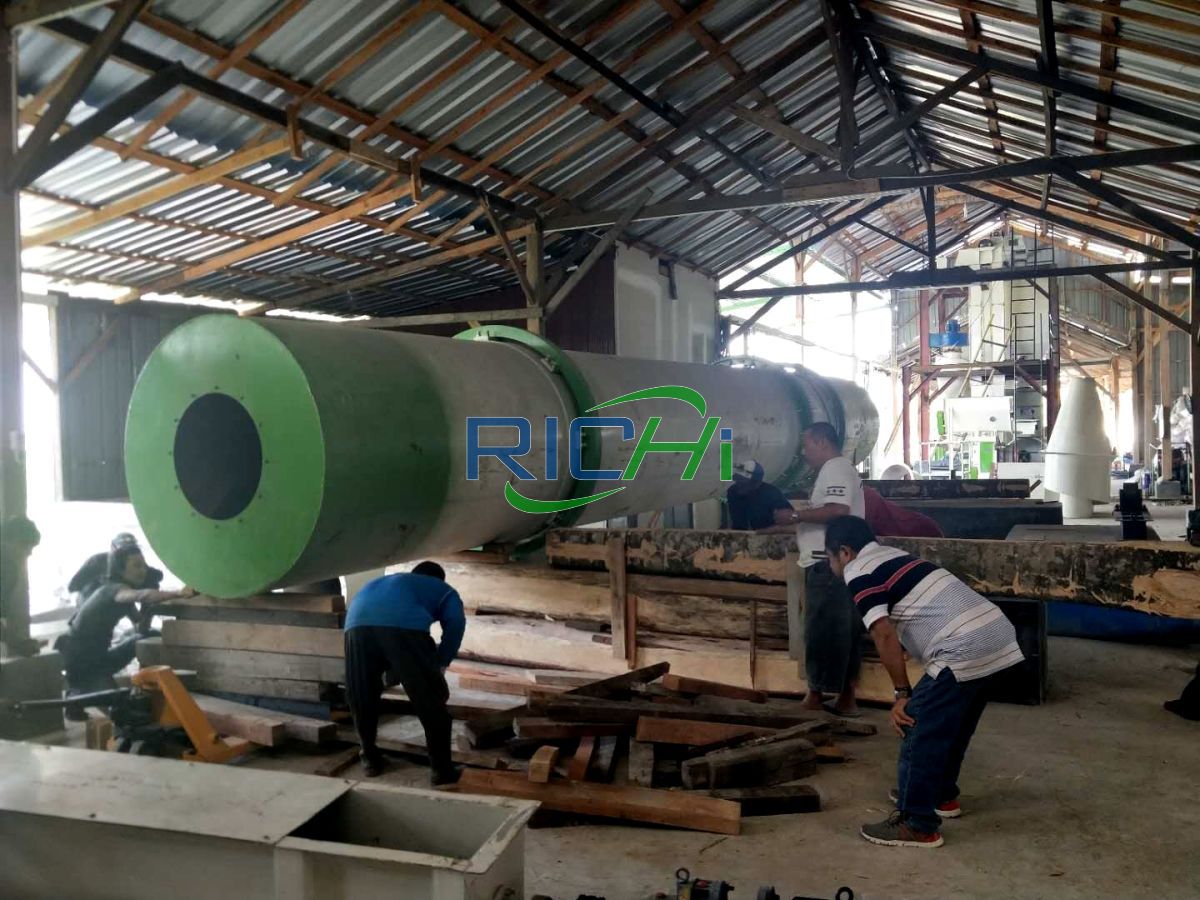
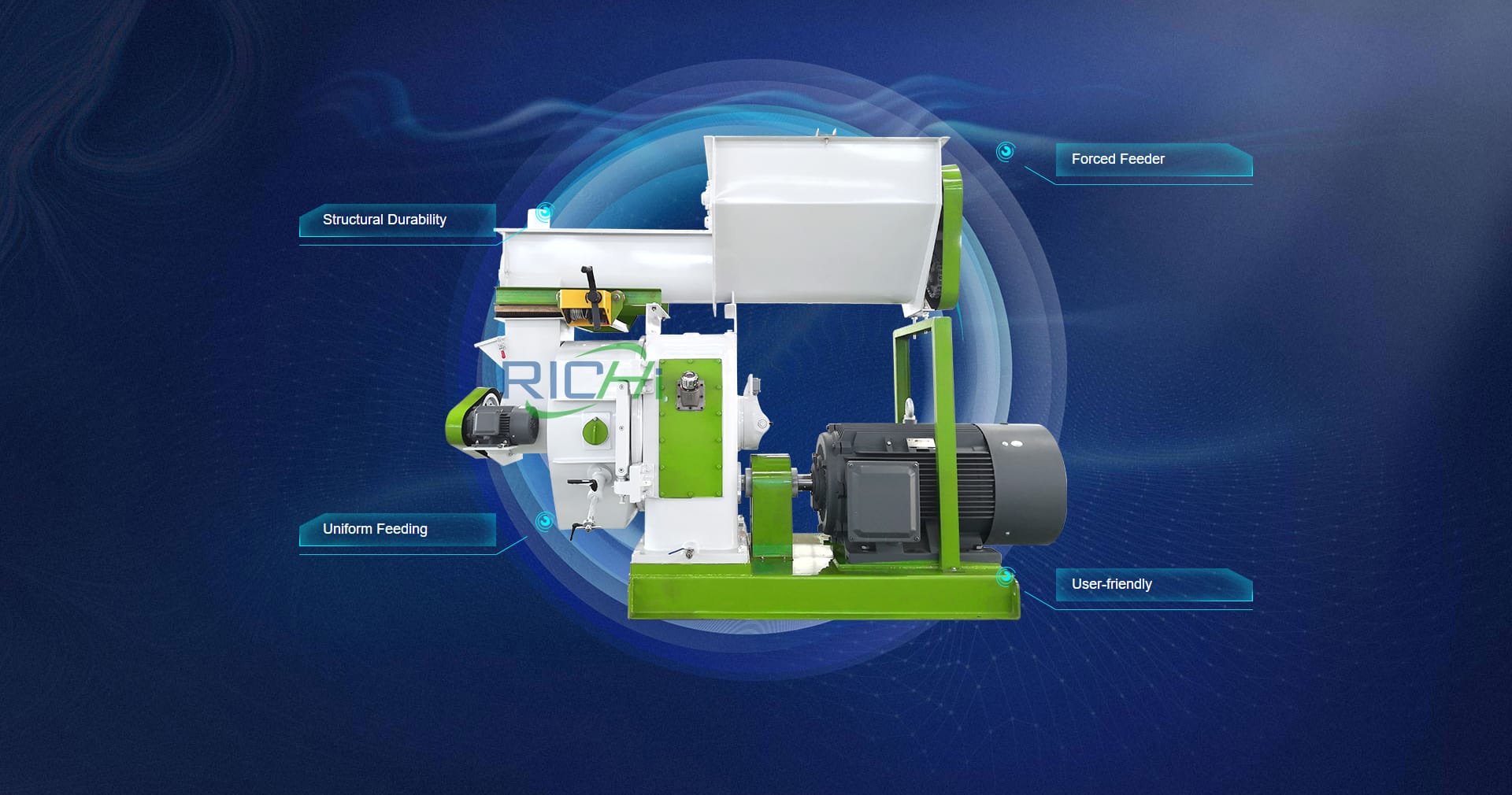
- Pellet Production Costs: The heart of the project lies in the pellet production facility, which includes the capital investment in equipment like pellet mills, coolers, and screening systems, as well as the ongoing operational costs associated with labor, maintenance, and utilities.
- Storage and Transportation Costs: Once produced, the biomass pellets need to be stored and transported to their end-use destinations, such as power plants or residential heating systems. These costs can vary based on the distance, mode of transportation, and storage requirements.
- Infrastructure and Site Preparation Costs: Depending on the project location, significant investments may be required for site preparation, utility connections, and supporting infrastructure, such as access roads and buildings.
- Permitting and Regulatory Costs: Biomass pellet projects are subject to various environmental and regulatory requirements, which can incur costs related to permitting, compliance, and monitoring.
- Financing Costs: Many biomass pellet projects require substantial upfront capital investments, necessitating financing options such as loans or equity investments. The associated interest rates and financing fees can significantly impact the overall project costs.
Factors Influencing Project Costs
While the cost components provide a general framework, the actual biomass pellet project cost can vary substantially due to several influencing factors:
- Project Scale: Larger projects often benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-unit cost of production. However, they also require higher upfront capital investments.
- Feedstock Availability and Quality: The availability and quality of the biomass feedstock can significantly impact preprocessing costs, transportation expenses, and overall pellet quality and yield.
- Technology and Equipment Selection: The choice of technology and equipment for pellet production, preprocessing, and supporting systems can greatly influence capital and operational costs, as well as efficiency and productivity.
- Location and Infrastructure: The project location can impact costs related to land acquisition, site preparation, transportation, and access to utilities and skilled labor.
- Regulatory Environment: Different regions may have varying regulatory requirements, permitting processes, and incentive programs, which can either increase or decrease project costs.
- Project Financing: The terms and conditions of project financing, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and equity contributions, can significantly impact the overall cost structure.
Cost Optimization and Risk Mitigation Strategies
To ensure the financial viability and success of biomass pellet projects, it is crucial to implement cost optimization and risk mitigation strategies. These may include:
- Feedstock Sourcing and Management: Establishing long-term contracts with reliable biomass suppliers, exploring alternative feedstock sources, and implementing efficient feedstock handling and storage systems can help mitigate supply risks and optimize costs.
- Process Optimization and Automation: Investing in advanced process control systems, automation technologies, and energy-efficient equipment can improve operational efficiency, reduce labor costs, and minimize waste.
- Strategic Project Siting: Carefully selecting project locations that offer access to abundant and cost-effective feedstock sources, existing infrastructure, and favorable regulatory environments can significantly reduce overall project costs.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Forming strategic partnerships with industry stakeholders, such as feedstock suppliers, technology providers, and end-users, can create synergies and leverage shared resources, reducing costs and risks.
- Financing Strategies: Exploring various financing options, such as government incentives, tax credits, and innovative financing models like power purchase agreements, can help mitigate financial risks and improve project economics.
- Risk Management and Contingency Planning: Implementing robust risk management strategies, including contingency planning for feedstock disruptions, equipment failures, and market fluctuations, can help mitigate potential cost overruns and project delays.
As the demand for renewable energy sources continues to grow, biomass pellet plant projects will play an increasingly vital role in the global energy transition. By carefully navigating the cost landscape and implementing effective cost optimization and risk mitigation strategies, project developers and stakeholders can unlock the full potential of this sustainable and versatile energy source, paving the way for a greener and more resilient future.